Content

On the other hand, liabilities are the total of current liabilities (short-term liabilities) and long-term liabilities. Current liability comprises debts that require repayment within one year, while long-term liabilities are liabilities whose repayment is due beyond one year. Equity typically refers to shareholders’ equity, which represents the residual value to shareholders after debts and liabilities have been settled. A company’s equity position can be found on its balance sheet, where there is an entry line for total equity on the right side of the table. Market analysts and investors prefer a balance between the amount of retained earnings that a company pays out to investors in the form of dividends and the amount retained to reinvest back into the company. A company’s equity represents its owners’ (shareholders’) residual claim to the company’s profits. You should note that if the resulting number is negative, then liabilities exceed assets and there is no equity left for the owners of the business.
- While the ratio cannot determine the optimal capital structure of a company, it can bring attention to an unsustainable reliance on debt financing which may soon lead to default .
- ROE is equal to a fiscal year net income , divided by total equity , expressed as a percentage.
- The equity ratio highlights two important financial concepts of a solvent and sustainable business.
- From the viewpoint of shareholders, treasury stock is a discretionary decision made by management to indirectly compensate equity holders.
- Equity can be found on a company’s balance sheet and is one of the most common pieces of data employed by analysts to assess a company’s financial health.
Retained earnings grow larger over time as the company continues to reinvest a portion of its income. The asset/equity ratio indicates the relationship of the total assets of the firm to the part owned by shareholders (aka, owner’s equity). This ratio is an indicator of the company’s leverage used to finance the firm.
💳 Payments
Stockholders’ equity is the value of a business’s assets that remain after subtracting liabilities. A company’s shareholders’ equity is fluid, often changing several times during a year due to actions taken by the company, which can affect one or more of the components. Current assets, such as cash, accounts receivables, and inventory, are assets that can be converted to cash within one year. Total assets are the sum of a company’s current assets and non-current assets. Stockholders’ equity is a line item that can be found on a company’s balance sheet, and the trend in stockholders’ equity can be assessed by looking at past balance sheet reports.
The way in which equity holders benefit is that the earnings per share increases from a lower share count, which can often lead to an “artificial” increase in the current share price upon a share repurchase. If the retained earnings balance turns negative, then the line item is titled “Accumulated Deficit”.
How Do You Calculate a Company’s Equity?
Thus, a shareholder concerned for his earnings will also be concerned for the company. Equity, as we have seen, has various meanings but usually represents ownership in an asset or a company, such as stockholders owning equity in a company. Subtract total liabilities from total assets to arrive at shareholder equity. The importance and value of the company’s asset/equity ratio is dependent upon the industry, the company’s assets and sales, current economic conditions, and other factors. There is no ideal asset/equity ratio value but it is valuable in comparing to similar businesses. A relatively high ratio may indicate the company has taken on substantial debt merely to remain its business. Current assets are generally liquid, or those which could be easily converted into cash in the short term, such as accounts receivable and inventory.
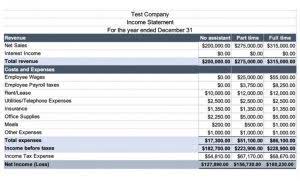
The equity ratio is aninvestment leverageorsolvency ratiothat measures the amount of assets that are financed by owners’ investments by comparing the total equity in the company to the total assets. Calculating stockholders equity is an important step in financial modeling. This is usually one of the last steps in forecasting the balance sheet items.
What does a debt-to-equity ratio of 1.5 mean?
The inverse of this calculation shows the amount of assets that were financed by debt. Companies with higher equity ratios show new investors and creditors that investors believe in the company and are willing to finance it with their investments.
Increased debt will make a positive contribution to a firm’s ROE only if the matching return on assets of that debt exceeds the interest rate on the debt. Equity is the value the how to calculate total equity business owners have in the business after all liabilities are paid. It is calculated by subtracting the value of all the liabilities from all the assets owned by the company.
Accounting
When examined along with these other benchmarks, the stockholders’ equity can help you formulate a complete picture of the company and make a wise investment decision. Lower stockholders’ equity is sometimes a sign that a firm needs to reduce its liabilities. For most companies, higher stockholders’ equity indicates more stable finances and more flexibility in case of an economic or financial downturn.
- The equity ratio is aninvestment leverageorsolvency ratiothat measures the amount of assets that are financed by owners’ investments by comparing the total equity in the company to the total assets.
- But an important distinction is that the decline in equity value occurs to the “book value of equity”, rather than the market value.
- Treasury shares or stock (not to be confused with U.S.Treasury bills) represent stock that the company has bought back from existing shareholders.
- Equity is the value the business owners have in the business after all liabilities are paid.
The corporation has 4,500 outstanding shares of preferred stock and 10,000 shares of common stock outstanding. Treasury shares or stock (not to be confused with U.S. Treasury bills) represent stock that the company has bought back from existing shareholders. Companies may do a repurchase when management cannot deploy all of the available equity capital in ways that might deliver the best returns. Shares bought back by companies become treasury shares, and the dollar value is noted in an account called treasury stock, a contra account to the accounts of investor capital and retained earnings. Shareholder equity can also indicate how well a company is generating profit, using ratios like the return on equity . This shows you the business’s net income divided by its shareholder equity, to measure the balance between investor equity and profit. It’s used in financial modeling to forecast future balance sheet items based on past performance.
Companies
If a company does liquidate, less marketable assets may yield lower sales proceeds than the value carried on the most recent balance sheet. The stockholders’ equity account is by no means a guaranteed residual value for shareholders if a company liquidated itself. Stockholders’ equity is the value of assets a company has remaining after eliminating all its liabilities. Companies with positive trending shareholder equity tend to be in good fiscal health. Those with negative trending shareholder’s equity could be in financial trouble, especially if they carry significant debt.

